The object oriented approach views off problem in terms of objects involved rather than procedure for doing it. Object oriented program names is defined as a method of implementation in which programs organised are cooperative collections of objects, each of which is an instance of some class.
The following general concept of oops are:
1) Object
2) Class
3) Data abstraction
4) Data encapsulation
5) Polymorphism
6) Dynamic binding
7) Message passing
8) Inheritance
1) Object: Object is an entity that can Store send and receive messages and an instance of a class. Each object contains both data and code to manipulate the data objects can interact without having to know details of each objects Data and code.
For eg: person, place and table etc.
2) Class: A class is a collection of objects that share common properties and relationships. For example you can think of a buses as objects. They have characteristics like steering wheel, motor, seats etc. And their behaviour is their mobility. However bus is not an object, it is a class.
Other example: we can say bird is a class but sparrow is an object.
3) Data Abstraction: Data abstraction refers to the act of representing essential features without including the background details or explanations for example you are driving a car.you only know the essential features to drive a car example gear handling, steering handling, use of clutch etc. But while driving you will not go into internal details of car like wiring, motor working etc.
4) Encapsulation: The wrapping of data and functions into single unit is known as encapsulation. Encapsulation is a way to implement data abstraction.
5) Inheritance: Inheritance is the process by which objects of one class acquire properties of objects of another class.a class which derived from another class is called derived class, a class which derived another class is called base class.
Inheritance is classified into following types:
a) Single inheritance: A method in which class derived from only one base class is called single inheritance.
b) Multiple inheritance: A method in which a class derived from several base classes is called multiple inheritance.
c) Hierarchical inheritance: A mechanism in which several classes are derived from single base class is called hierarchical inheritance.
d) Multilevel inheritance: The mechanism of deriving a class from another derived class is known as multilevel inheritance.
5) Hybrid inheritance: Mechanism of deriving a class from several other derived classes.
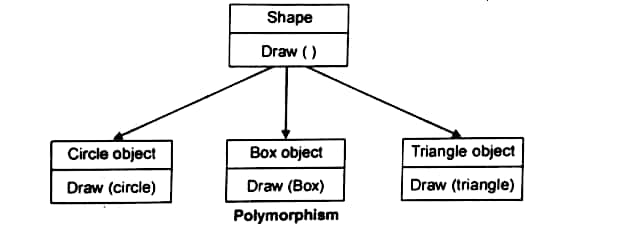
6) Polymorphism: Polymorphism is made up of two words "poly+ morphism" where:
poly means "many"
morphism means "forms"
polymorphism is a process of defining a number of objects of different classes into a group and call the member function to carry out the operation of the objects using different functions polymorphism means the ability to take more than one form.
7) Dynamic Binding: Dynamic binding means to link the procedure call to the cord to be executed in response to the call. Dynamic binding means that the cord associated with the given procedure call is not known until the time of the call at runtime. It is associated with polymorphism and inheritance.
Nice and easy to grasp.
ReplyDeleteStrange "water hack" burns 2lbs overnight
ReplyDeleteMore than 160k women and men are using a simple and SECRET "liquids hack" to drop 2lbs each and every night in their sleep.
It is scientific and works on everybody.
Just follow these easy step:
1) Take a drinking glass and fill it up with water half the way
2) Now learn this crazy hack
and become 2lbs skinnier as soon as tomorrow!